Most of your website traffic shows up as “unknown” in analytics.
Visitors come, browse a few pages, and leave without filling out a form or signing up.
These are called anonymous website visitors, and they often make up more than 90% of total traffic.
Ignoring them is like fishing with holes in your net, you’ll lose the biggest catch.
In this guide, we’ll break down what anonymous visitors are, why they matter, and how you can identify and track them without crossing privacy lines.
Key Takeaways
Most visitors leave without engaging, so uncovering who they are helps businesses capture potential leads. By analyzing their behavior, companies can connect anonymous traffic to real opportunities.
Using IP intelligence, visitor analytics, and firmographic data, businesses can identify organizations browsing their site. This helps align outreach with interested companies even when individuals remain anonymous.
Lightweight tracking protects privacy but offers limited insights. Advanced tracking allows deeper analysis with features like heatmaps, session replays, and visitor history to understand intent and improve conversions.
Usermetric’s advanced mode links visitor behavior with identifiers like custom parameters, UTMs, and goals. This equips marketing and sales teams with actionable insights for lead generation and campaign optimization.
Cookieless analytics, AI-driven insights, and evolving privacy laws are redefining how businesses study visitor behavior. The future points to smarter, privacy-conscious tracking that still delivers valuable insights.
What Are Anonymous Website Visitors and Why Do They Matter?
Anonymous visitors are users who land on your site but don’t provide any identifiable information, such as names or email addresses.
They remain invisible in traditional analytics tools, yet they are a goldmine of untapped opportunities.
How do anonymous web visitors differ from known visitors?
Anonymous web visitors are those you can’t directly tie to a profile or contact detail.
Known visitors, on the other hand, usually share information through forms, sign-ups, or logins.
The key difference is that anonymous traffic still interacts with your site, they read articles, click buttons, and browse products.
You just can’t connect those behaviors to a specific identity.
Think of it this way:
- Known visitors = people who shake your hand and tell you their name.
- Anonymous visitors = people who attend your event but leave without introducing themselves.
Both groups are in the room, but only one makes it onto your contact list.
Why does most website traffic appear anonymous in analytics tools?
Most traffic looks anonymous because standard analytics platforms track sessions, not identities.
Unless someone voluntarily shares personal data, tools like Google Analytics categorize them as “unknown.”
There are several reasons for this:
- No form submissions → users read but don’t engage.
- Cookie restrictions → browsers block tracking scripts.
- Privacy laws → tools anonymize IP addresses.
- Short visits → users bounce before interaction.
In short, the web is designed to make users anonymous by default, and analytics only reveals what you explicitly collect.
What business opportunities are lost if you ignore anonymous traffic?
If you ignore anonymous website traffic, you lose insights into the majority of your audience.
This blind spot means:
- Missed leads: You don’t know which companies are browsing your site.
- Poor targeting: Campaigns run without understanding visitor behavior.
- Lower conversions: Visitors leave without nudges to act.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Ignoring Anonymous Visitors | Tracking Anonymous Visitors |
|---|---|
| 90%+ of traffic wasted | More leads identified |
| Blind spots in user journey | Clear behavior analysis |
| Less ROI from marketing | Higher conversion potential |
By tracking anonymous visitors, businesses can turn silent clicks into real opportunities.
How Can You Identify Anonymous Website Traffic Without Forms?
Even without forms, there are ways to learn about your anonymous audience.
You may not know “John Smith from New York,” but you can discover patterns, behaviors, and even company-level data.
What role do IP addresses and company lookups play in visitor tracking?
IP addresses can reveal general location and sometimes the organization behind the traffic.
With company lookups, you can match an IP to a business, giving sales teams valuable insight into which firms are showing interest.
For example, if an IP lookup shows multiple visits from a Fortune 500 company, you instantly know there’s warm interest, even if individuals remain anonymous.
However, IP tracking has limits:
- Dynamic IPs can change frequently.
- VPNs hide real addresses.
- Privacy laws restrict storing IPs in raw form.
Still, company-level insights remain one of the most powerful ways to uncover the business intent behind anonymous visits.
How do cookies and session identifiers uncover repeat anonymous visitors?
Cookies and session identifiers let you track visitors across multiple sessions, even if you don’t know who they are.
- Cookies: Small files stored in the browser that help recognize returning visitors.
- Session IDs: Temporary identifiers that connect actions during one visit.
With these, you can tell if an anonymous user:
- Came back three times this week.
- Visited the pricing page repeatedly.
- Abandoned a cart multiple times.
This creates a behavioral fingerprint, which is useful for personalization and retargeting.
But, of course, cookies come with compliance challenges (GDPR and CCPA require consent).
Can you track website visitor behavior without personal information?
Yes, absolutely.
Anonymous tracking doesn’t always mean personal identification.
You can still gather valuable insights without knowing names or emails.
Some non-intrusive methods include:
- Pageview analytics: Which content gets the most attention.
- Click tracking: Which CTAs are most effective.
- Engagement metrics: Time on site, scroll depth, bounce rates.
This type of tracking answers key questions like:
- Which pages make people leave?
- What path do users take before converting?
- Which traffic source brings engaged visitors?
By focusing on behavior rather than identity, businesses get actionable insights while maintaining user trust.
Which Tools Help With Anonymous Website Visitor Tracking?
Not all analytics tools handle anonymous traffic equally.
Some just report numbers, while others provide deep behavioral insights or even company-level identification.
What features should you look for in an anonymous tracking tool?
When choosing a tool for anonymous visitor tracking, look for:
- Company identification: Match visits to organizations.
- Behavior analysis: Heatmaps, session replays, clicks.
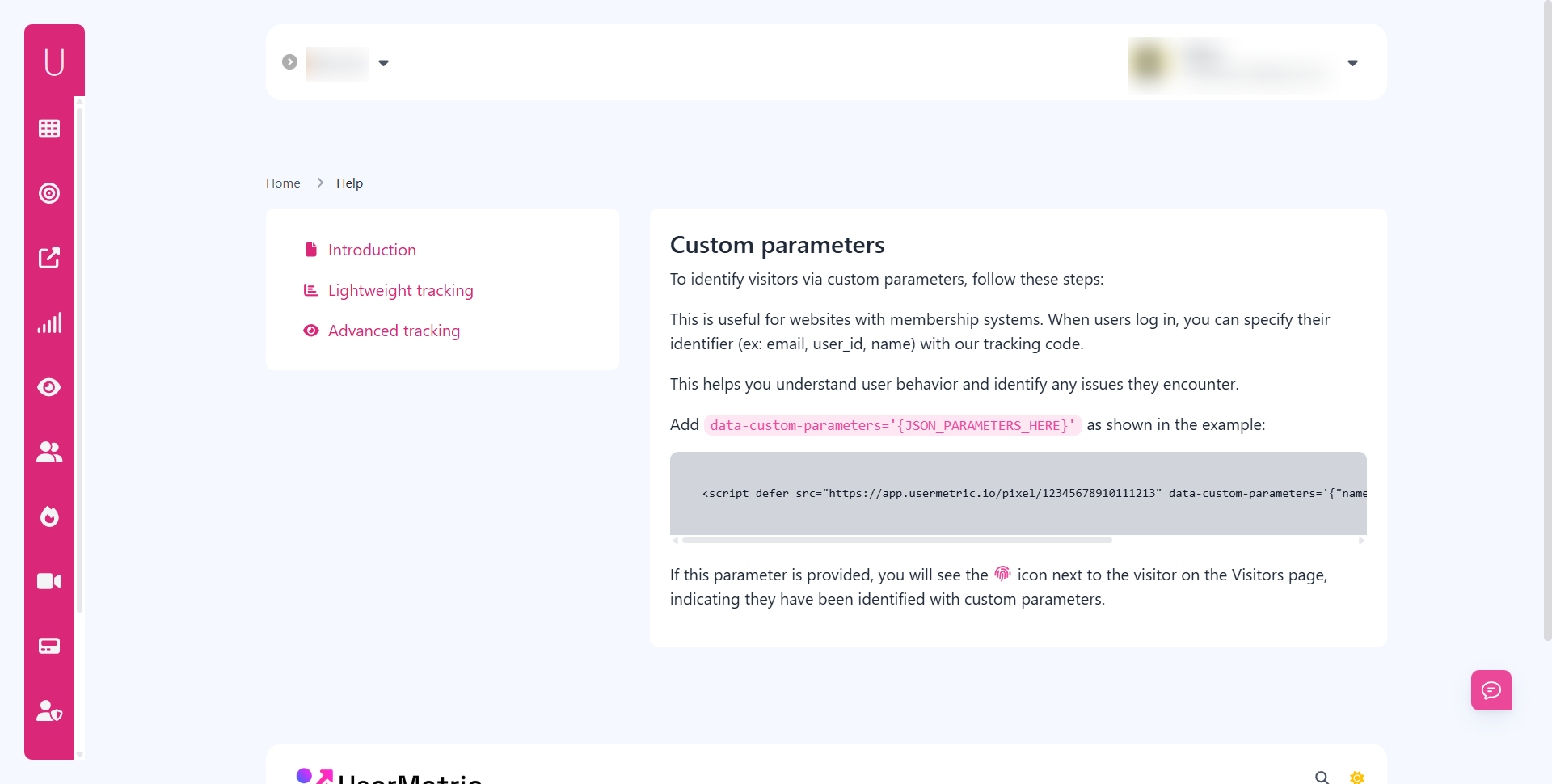
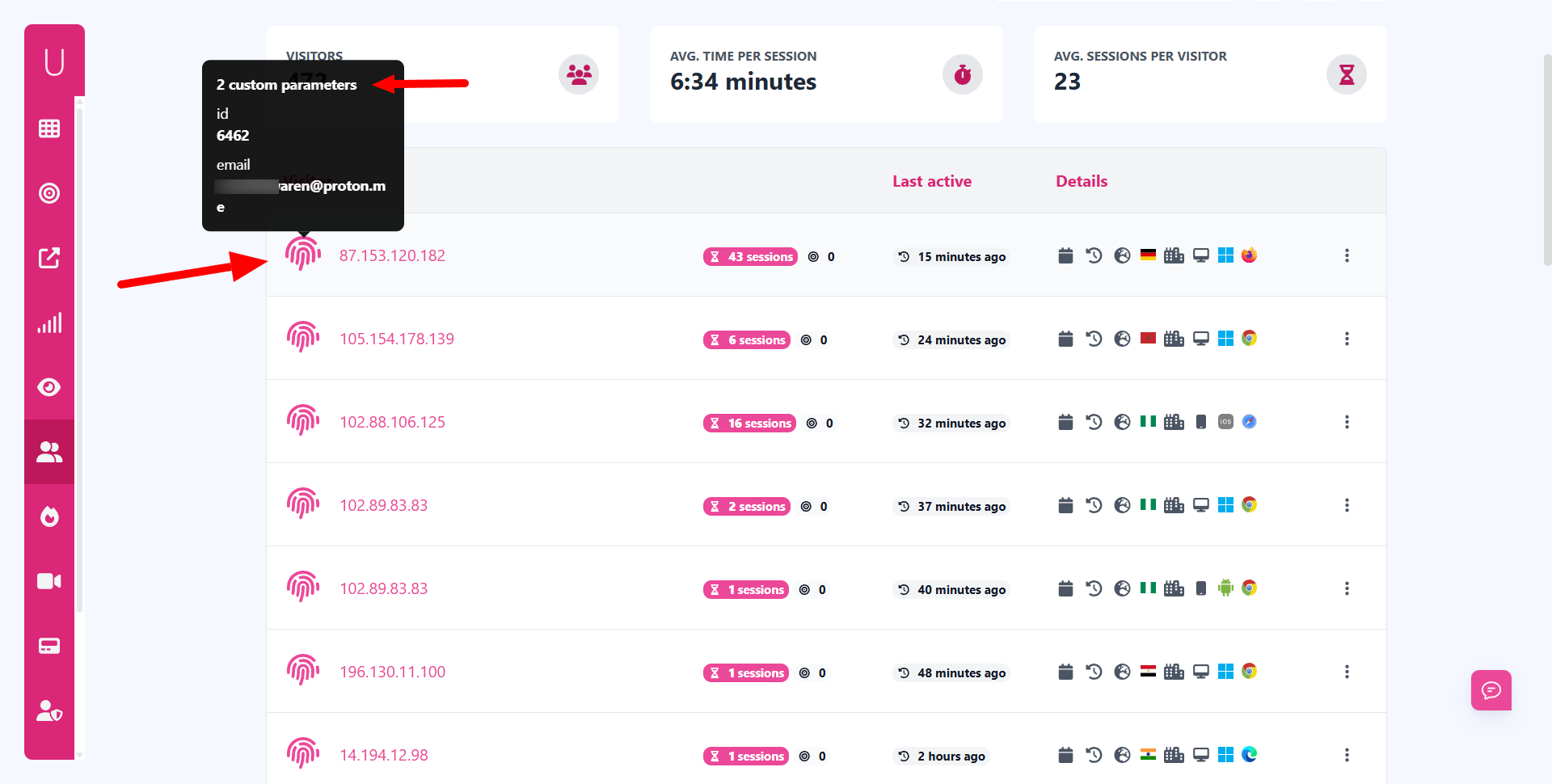
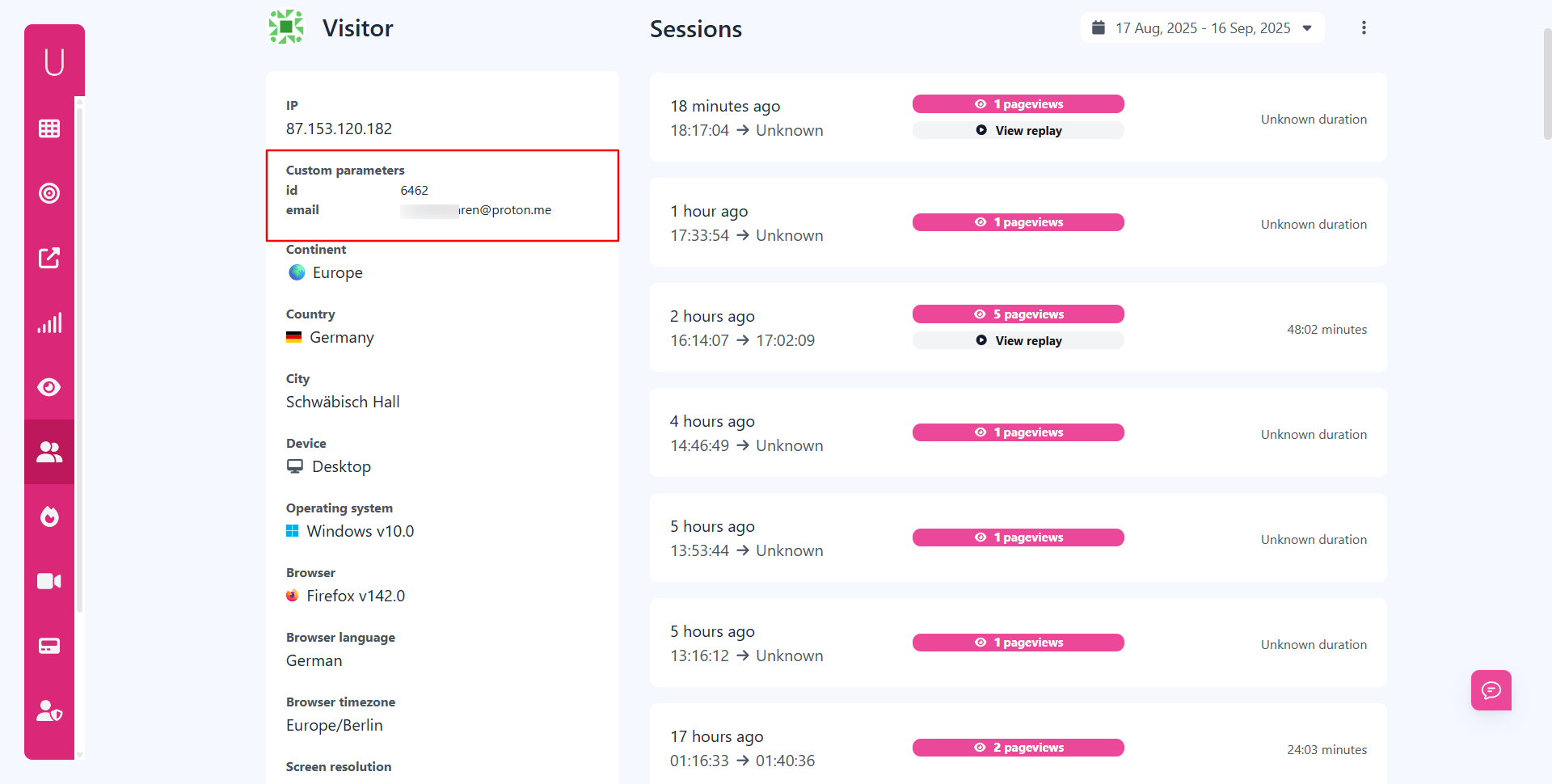
- Custom parameters: Tag visitors with extra data.
- Integration support: Connect with CRM and sales platforms.
- Privacy compliance: Built-in GDPR and CCPA support.
A solid tool doesn’t just show that someone visited, it explains who they might be, what they did, and why it matters.
How does Usermetric track anonymous web visitors compared to Google Analytics?
Google Analytics is great for aggregate data but weak on anonymous visitor insights.
It shows pageviews, sessions, and bounce rates but can’t tie behavior to specific companies or individuals.
Usermetric, on the other hand, goes deeper:
- Advanced tracking mode: Identifies repeat anonymous visitors using session history.
- Custom parameters: Lets businesses add user IDs or tags.
- Privacy options: Complies with DNT and consent requirements.
While Google Analytics answers “How much traffic do I have?”, Usermetric answers “Who’s behind that traffic, and what are they doing?”
What are the pros and cons of different anonymous tracking solutions?
Here’s a side-by-side look at popular approaches:
| Approach | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Google Analytics | Free, widely used, great for trends | Weak on identity, limited insights |
| IP & Company Lookups | Reveals organizations, B2B-friendly | VPNs/Dynamic IPs reduce accuracy |
| Usermetric Advanced Mode | In-depth behavior + IP tracking + custom data | Requires consent for personal tracking |
| Lightweight Tracking | Cookie-free, privacy-first, fast | No session history, limited features |
The right choice depends on your goals.
If you want compliance-friendly insights, lightweight tracking works.
If you want business intelligence from anonymous visitors, advanced solutions like Usermetric shine.
How Do You Balance Privacy With Tracking Anonymous Visitors?
Tracking anonymous users always comes with a question: how do you gain insights without breaking trust?
The answer lies in understanding the difference between tracking for insights and tracking for identification.
What is the difference between anonymous tracking and privacy-first analytics?
Anonymous tracking focuses on behavioral insights without identity.
Privacy-first analytics, on the other hand, ensures that data collection avoids personal identifiers like names, emails, or raw IPs.
In short:
- Anonymous tracking = find patterns in unknown traffic.
- Privacy-first analytics = collect only what you need, with user respect.
Businesses should combine both: get the insights while keeping personal information safe.
How do GDPR, CCPA, and PECR affect anonymous website visitor tracking?
These privacy laws set rules on how businesses handle user data:
- GDPR (Europe): Requires consent for cookies, IPs, or personal data.
- CCPA (California): Gives users the right to opt out of data collection.
- PECR (UK/EU): Covers cookie usage and electronic communications.
If your tool processes anonymous traffic in a way that links it to identifiable individuals, you must get consent.
But if you only collect aggregated or non-identifiable behavior data, you can usually operate without it.
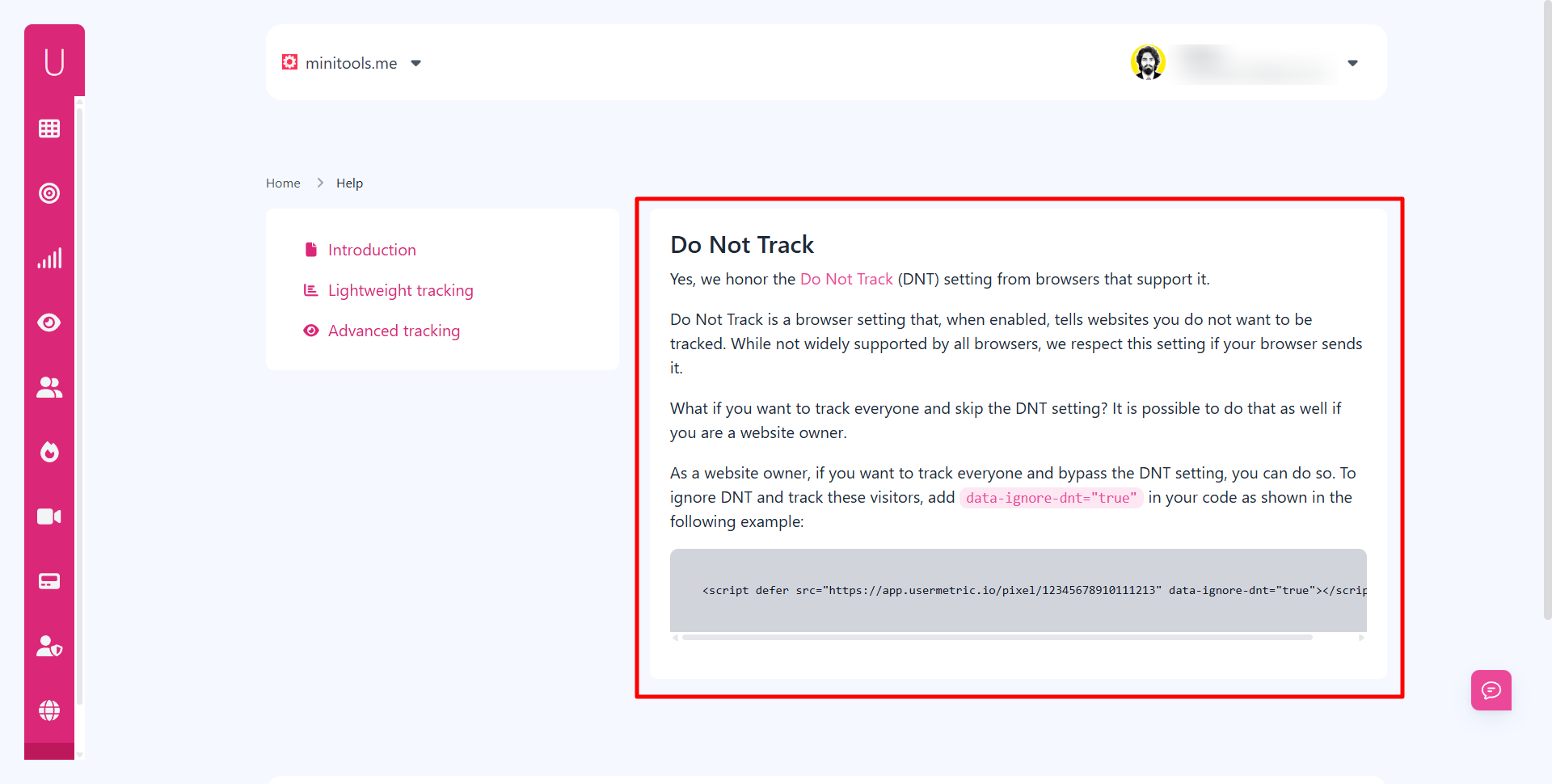
Can businesses respect Do Not Track (DNT) while analyzing anonymous visitors?
Yes, businesses can honor DNT signals and still analyze anonymous traffic.
Tools like Usermetric support DNT, meaning if a user enables it in their browser, they won’t be tracked.
This provides a balance:
- Users who value privacy get it.
- Businesses still gather data from the majority of visitors.
By respecting DNT, businesses not only stay compliant but also build trust with their audience.
What Strategies Help Turn Anonymous Website Visitors Into Leads?
Turning anonymous website traffic into leads is all about uncovering intent and offering value at the right time.
You may not know who the individual is, but you can use technology, behavior analysis, and smart engagement to transform silent clicks into real opportunities.
How can you identify companies behind anonymous traffic?
You can identify companies behind anonymous traffic by analyzing IP addresses and matching them to known organizations.
This process is called IP-to-company resolution and is a powerful way to reveal B2B interest.
For example, if several visits originate from the same IP belonging to a financial firm, you know that company is exploring your services, even if you don’t know the exact employee.
Pairing this with referral data and browsing behavior helps narrow down what they are researching.
The benefit here is simple: you can prioritize outreach to businesses already showing intent.
Sales teams no longer need to cold-call blindly, they can follow up with warm leads.
What role does visitor behavior analysis play in conversion tracking?
Visitor behavior analysis highlights what anonymous users do before leaving your site, helping you understand intent and drop-off points.
By mapping these behaviors, you can connect anonymous activity with potential buying signals.
Some key behaviors to watch include:
- Time spent on pricing pages → shows strong intent.
- Repeated visits to product pages → suggests interest in comparison.
- Engagement with blog or resource sections → indicates research stage.
When you track these behaviors, you create a conversion funnel for unknown visitors.
Even without knowing their name, you can tell whether they are casual browsers or serious buyers.
Which engagement tactics work best for converting anonymous web visitors?
The best tactics for converting anonymous visitors involve lowering friction and offering value upfront.
Since you don’t know them yet, your goal is to encourage micro-conversions that build trust.
Some effective engagement strategies include:
- Personalized CTAs: Suggest relevant guides or offers based on page behavior.
- Exit-intent popups: Offer discounts, free trials, or resources before they leave.
- Interactive tools: Calculators, quizzes, or demos that capture light details (like email).
- Retargeting ads: Reach anonymous visitors after they leave with personalized campaigns.
These tactics gradually move users from being unknown browsers to qualified leads.
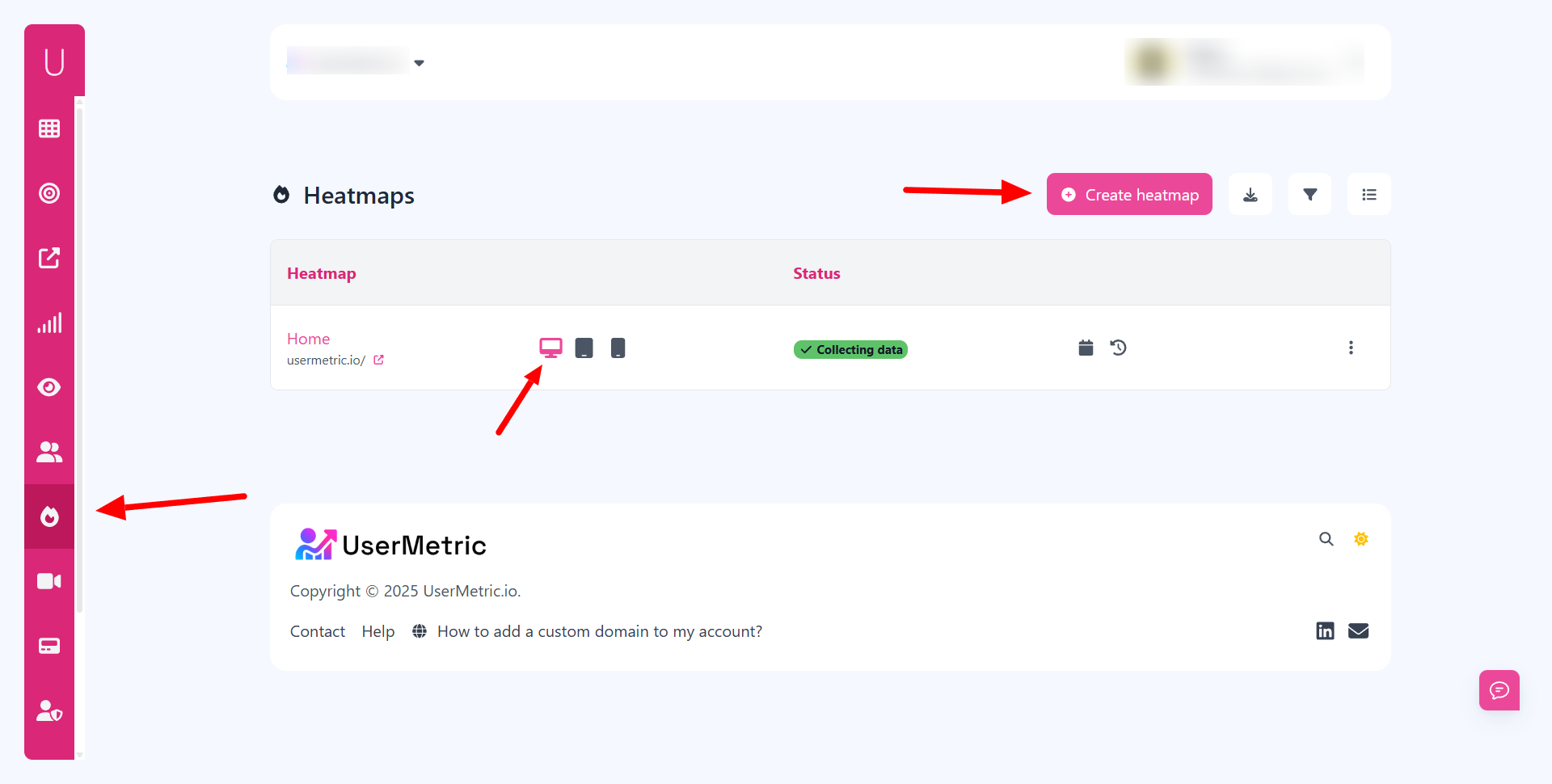
How Does Usermetric Help With Advanced Anonymous Visitor Tracking?
Usermetric offers two modes, lightweight tracking for privacy-first analytics and advanced tracking for businesses that need deeper insights.
To identify anonymous visitors effectively, the advanced mode provides the necessary features.
Why is advanced tracking needed for identifying anonymous visitors?
Advanced tracking is required because lightweight tracking avoids storing identifiers, which means you can’t connect sessions or recognize repeat visitors.
For businesses, this limits the ability to analyze and convert anonymous traffic.
With advanced tracking, however, you can:
- Identify repeat sessions.
- Capture custom parameters like user IDs.
- Record detailed visitor paths.
This transforms “unknown” clicks into actionable data for sales and marketing teams.
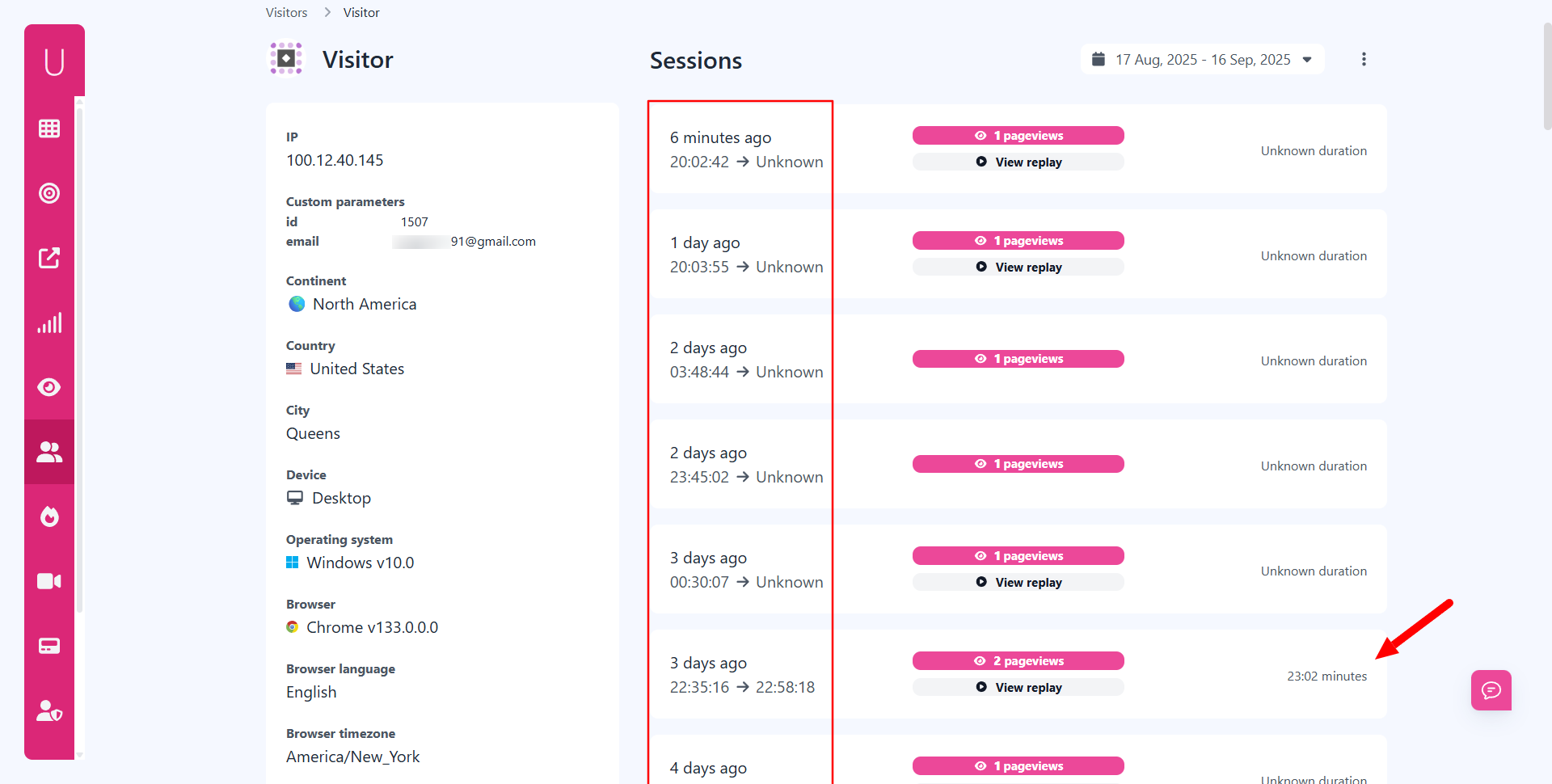
What insights can Usermetric provide beyond lightweight tracking?
Beyond basic traffic numbers, Usermetric’s advanced tracking provides deep visitor insights that lightweight tracking can’t capture.
These include:
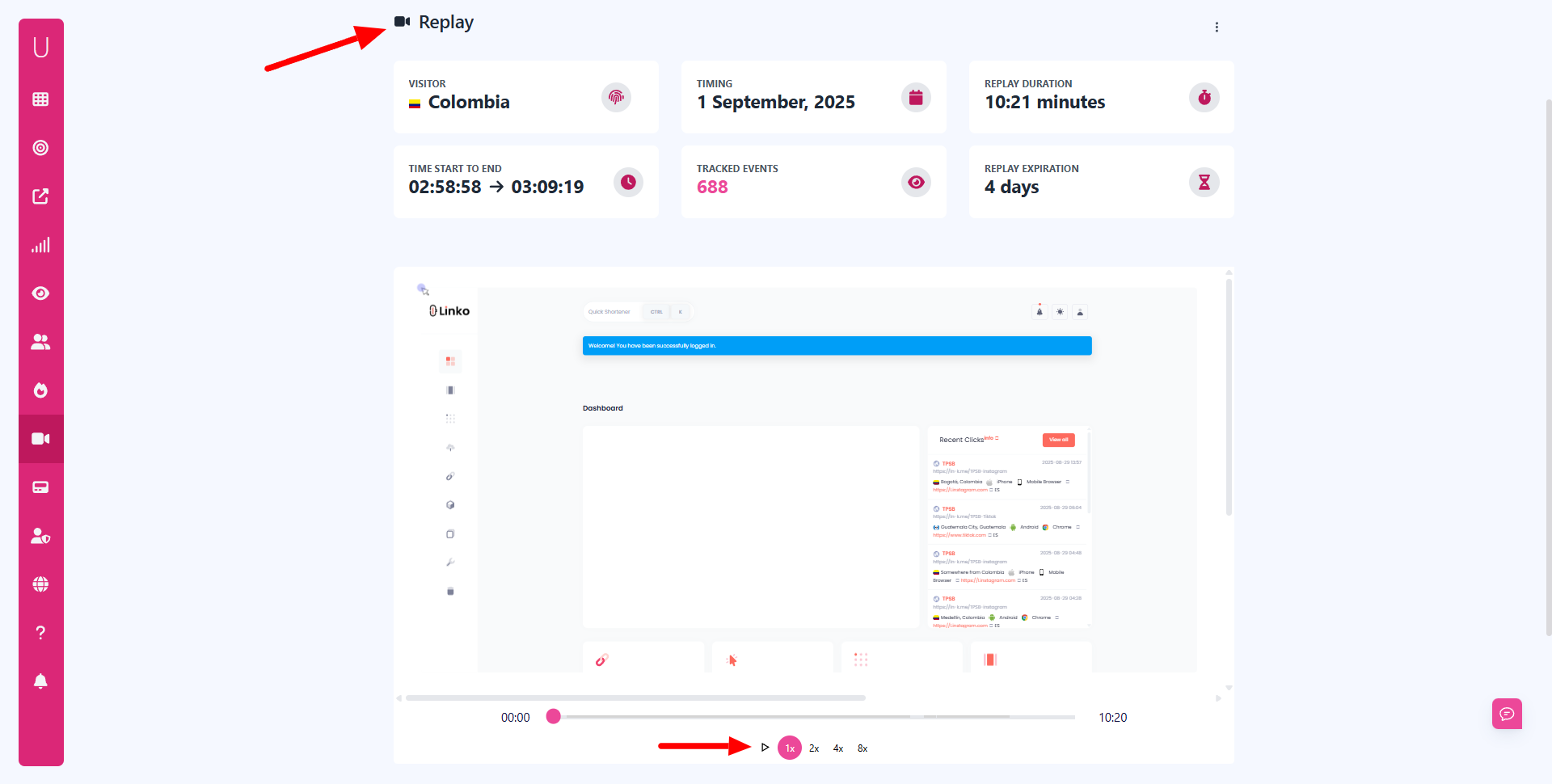
- Session replays and heatmaps → watch how visitors interact with pages.
- Custom parameters → tag users with internal IDs or membership details.
- Goal tracking → monitor clicks, downloads, and form interactions.
Unlike lightweight analytics, advanced tracking gives you the context behind the numbers, making it possible to act on what anonymous visitors actually do.
How can teams use Usermetric data to improve marketing and sales?
Teams can use Usermetric data to align marketing campaigns with real visitor behavior and help sales prioritize outreach.
By understanding which businesses and individuals show the most engagement, you can direct resources more effectively.
For example:
- Marketing teams can refine campaigns based on content that anonymous users engage with most.
- Sales teams can follow up with companies that repeatedly visit pricing or product pages.
- Product teams can improve UX by analyzing session replays and heatmaps.
In short, Usermetric’s advanced tracking bridges the gap between anonymous interest and qualified leads.
What Are the Future Trends in Anonymous Website Visitor Tracking?
The landscape of tracking is evolving.
With growing privacy regulations and changes in browser technology, businesses need smarter, more respectful ways to analyze anonymous website traffic.
How will cookieless tracking change the way we analyze website traffic?
Cookieless tracking will shift focus from individual identifiers to aggregated, event-based data.
Instead of following one person across multiple visits, tools will rely on contextual signals.
This means analytics will emphasize:
- Session-level behavior rather than personal data.
- Event triggers like clicks and scrolls.
- Aggregated cohorts instead of one-to-one tracking.
The upside is that businesses can still measure performance, but in a way that prioritizes speed and privacy.
What role will AI play in understanding anonymous visitor behavior?
AI will play a growing role by turning raw, anonymous activity into patterns that humans can act on.
Rather than needing identity, machine learning can identify clusters of behavior.
AI can help by:
- Predicting which anonymous users are most likely to convert.
- Personalizing content based on behavior, not cookies.
- Automating lead scoring for anonymous traffic.
With AI, businesses won’t just see what happened, they’ll understand why it matters.
Is anonymous tracking becoming harder or easier under new privacy laws?
Anonymous tracking is both harder and easier under privacy laws.
It’s harder because businesses can no longer rely on invasive methods like third-party cookies.
But it’s easier in the sense that new tools are being built for compliance by design.
Privacy laws encourage businesses to:
- Be transparent with users.
- Collect only the data necessary.
- Provide opt-out options.
Instead of resisting these changes, companies that adopt privacy-first tracking tools can stay ahead while still unlocking valuable insights from anonymous visitors.
Final Thoughts
Anonymous website visitors may seem invisible at first, but with the right tools and strategies, they become one of the most valuable parts of your traffic.
By combining behavior analysis, company lookups, and engagement tactics, you can transform anonymous clicks into leads and customers.
Platforms like Usermetric make this process easier by offering both lightweight and advanced tracking modes, giving you the flexibility to balance privacy with actionable insights.
The future of anonymous tracking is clear: businesses that respect privacy while uncovering visitor intent will build more trust, convert more leads, and grow faster.
FAQs
Can I ever fully identify anonymous website visitors?
Not always. You can uncover company-level insights and behavioral data, but full personal identification requires voluntary data sharing (like form fills).
Is anonymous visitor tracking legal?
Yes, as long as it complies with GDPR, CCPA, and other laws. Collect only necessary data, anonymize where possible, and honor opt-outs.
Do I need cookies to track anonymous visitors?
Not necessarily. Cookieless tracking can analyze events and behavior without storing identifiers, though cookies help with session history.
How is Usermetric different from Google Analytics for anonymous tracking?
Google Analytics focuses on aggregate data, while Usermetric’s advanced tracking mode reveals deeper insights such as repeat visits, and behavior analysis.
What’s the best way to convert anonymous traffic into leads?
The best way is to use behavior-driven engagement tactics like personalized CTAs, exit-intent popups, and retargeting ads to encourage anonymous users to share contact details.

